Grading of Lattice Structures for Stiffness Optimization: A Topology Optimization-Based Approach for Parts Manufactured via Multi Jet Fusion
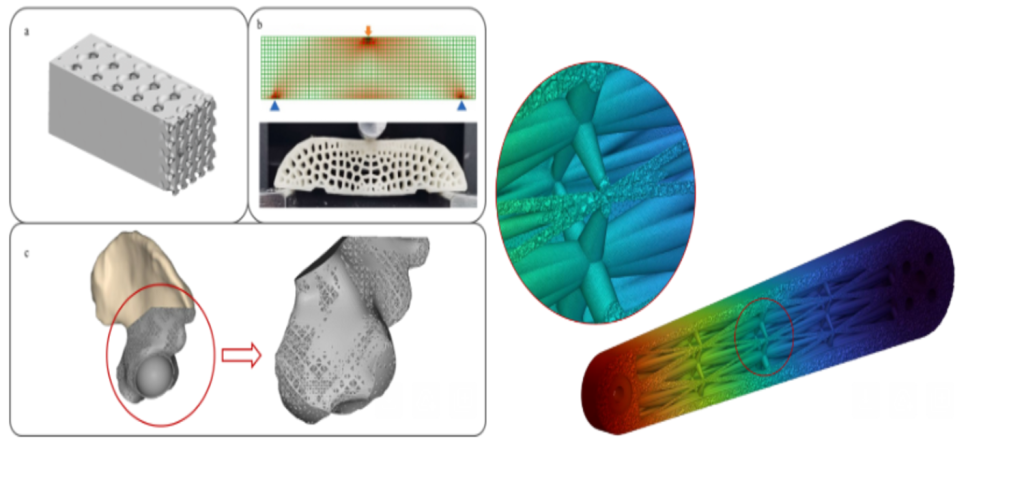
In this work, published in Dyna, a method for optimizing lattice structures manufactured using 3D printing with the Multi Jet Fusion (MJF) technique was investigated, aiming to reduce weight and maximize stiffness in mechanical components. The developed workflow combined field-driven topology optimization and the automation of nTop software using Python scripts, allowing the local variation of strut diameters in lattice structures based on computationally generated density maps. This method was applied to a connecting rod, evaluating load conditions through finite element analysis (FEA) to validate the optimized mechanical performance. The results showed a 24.2% mass reduction and a moderate 14% increase in deformation, while maintaining high accuracy between simplified and full models (average deviation of 7.6%). This innovative approach balances computational efficiency and advanced design, offering a promising tool for optimizing lightweight components across various industries through additive manufacturing.