Substrate integration in stainless steel components fabricated by plasma arc-directed energy deposition
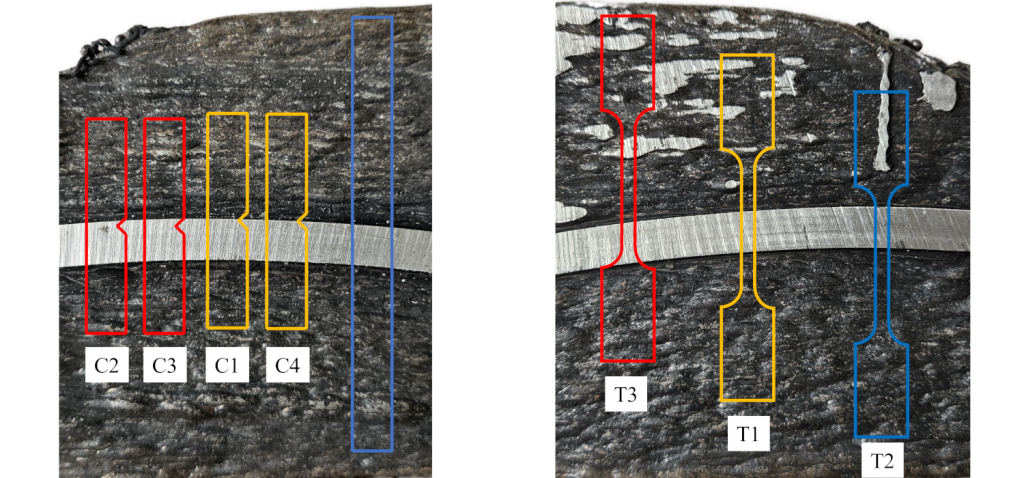
Directed energy deposition process needs a substrate, as a base for depositing layers of material, which is discarded after manufacturing. This study showed the feasibility of incorporating a substrate into the final product to reduce material waste and energy. For this purpose, double sided walls-substrate austenitic stainless steel structures were produced by Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing (WAAM). To assess the viability of this approach, mechanical tests such as tensile, hardness, and impact flexure tests were conducted on printed specimens, which were extracted through electrical discharge machining. This was completed with a fractographic analysis of the tested samples. A metallographic analysis was also performed both to assess the internal structure and to evaluate the effects of substrate integration on mechanical properties, thus showing various structural transitions across the bead-substrate interface, including the presence of vermicular and skeletal ferrite within an austenitic matrix. An EDX analysis showed chemical composition variations across the interface. Additionally, energy and cost assessments showed an 8% reduction in material usage, an 8.7% reduction in manufacturing time and an 8.4% reduction in energy consumption and associated emissions through substrate integration. The results confirmed the feasibility of integrating substrates into WAAM-fabricated components while maintaining mechanical characteristics within the expected range for stainless steel structures.